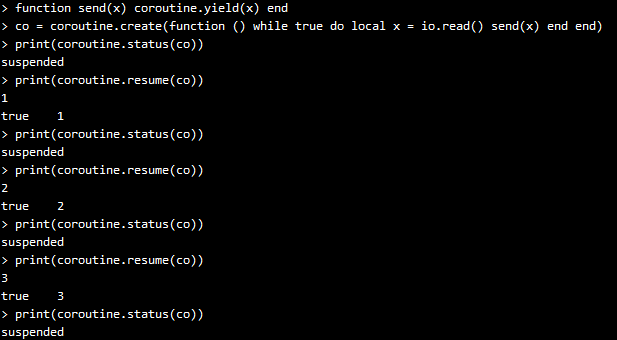
Lua的coroutine 跟thread 的概念比较相似,但是也不完全相同。一个multi-thread的程序,可以同时有多个thread 在运行,但是一个multi-coroutines的程序,同一时间只能有一个coroutine 在运行,而且当前正在运行的coroutine 只有在被显式地要求挂起时,才会挂起。Lua的coroutine 是一个强大的概念,尽管它的几个主要应用都比较复杂。
Lua将coroutine相关的所有函数封装在表coroutine 中。create 函数,创建一个coroutine ,以该coroutine 将要运行的函数作为参数,返回类型为thread 。
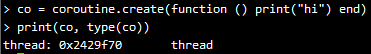
coroutine 有4个不同的状态:suspended, running, dead, normal。当新create 一个coroutine的时候,它的状态为suspended,意味着在create 完成后,该coroutine 并没有立即运行。我们可以用函数status 来查看该coroutine 的状态:
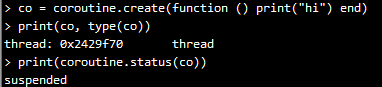
函数coroutine.resume (恢复)运行该coroutine,将其状态从suspended变为running:
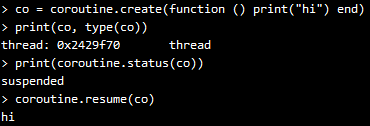
在该示例中,该coroutine运行,简单地输出一个“hi”就结束了,该coroutine变为dead状态:
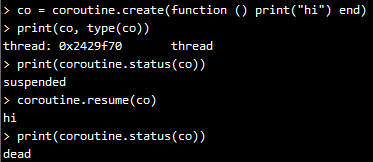
到目前为止,coroutine看起来好像也就这么回事,类似函数调用,但是更复杂的函数调用。但是,coroutine的真正强大之处在于它的yield 函数,它可以将正在运行的coroutine 挂起,并可以在适当的时候再重新被唤醒,然后继续运行。下面,我们先看一个简单的示例:
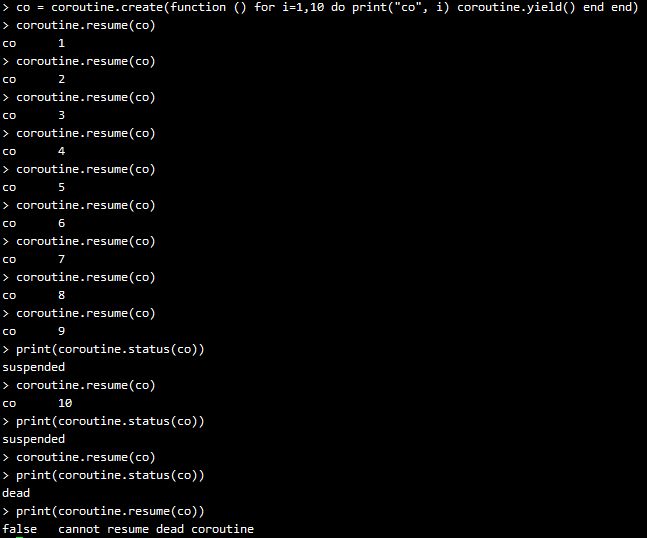
我们一步一步来讲,该coroutine每打印一行,都会被挂起,看起来是不是在运行yield 函数的时候被挂起了呢?当我们用resume 唤醒该coroutine时,该coroutine继续运行,打印出下一行。直到最后没有东西打印出来的时候,该coroutine退出循环,变为dead状态(注意最后那里的状态变化)。如果对一个dead状态的coroutine进行resume 操作,那么resume会返回false+err_msg,如上面最后两行所示。
注意,resume 是运行在protected mode下。当coroutine内部发生错误时,Lua会将错误信息返回给resume 调用。
当一个coroutine A在resume另一个coroutine B时,A的状态没有变为suspended,我们不能去resume它;但是它也不是running状态,因为当前正在running的是B。这时A的状态其实就是normal 状态了。
Lua的一个很有用的功能,resume-yield对,可以用来交换数据。下面是4个小示例:
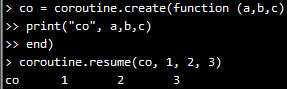
1)main函数中没有yield,调用resume时,多余的参数,都被传递给main函数作为参数,下面的示例,1 2 3分别就是a b c的值了:
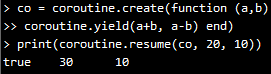
2)main函数中有yield,所有被传递给yield的参数,都被返回。因此resume的返回值,除了标志正确运行的true外,还有传递给yield的参数值:
3)yield也会把多余的参数返回给对应的resume,如下:
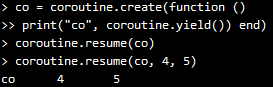
为啥第一个resume没有任何输出呢?我的答案是,yield没有返回,print就根本还没运行。
4)当一个coroutine结束的时候,main函数的所有返回值都被返回给resume:
![]()
我们在同一个coroutine中,很少会将上面介绍的这些功能全都用上,但是所有这些功能都是很useful的。
目前为止,我们已经了解了Lua中coroutine的一些知识了。下面我们需要明确几个概念。Lua提供的是asymmetric coroutine,意思是说,它需要一个函数(yield)来挂起一个coroutine,但需要另一个函数(resume)来唤醒这个被挂起的coroutine。对应的,一些语言提供了symmetric coroutine,用来切换当前coroutine的函数只有一个。
有人想把Lua的coroutine称为semi-coroutine,但是这个词已经被用作别的意义了,用来表示一个被限制了一些功能来实现出来的coroutine,这样的coroutine,只有在一个coroutine的调用堆栈中,没有剩余任何挂起的调用时,才会被挂起,换句话说,就是只有main可以挂起。Python中的generator好像就是这样一个类似的semi-coroutine。
跟asymmetric coroutine和symmetric coroutine的区别不同,coroutine和generator(Python中的)的不同在于,generator并么有coroutine的功能强大,一些用coroutine可实现的有趣的功能,用generator是实现不了的。Lua提供了一个功能完整的coroutine,如果有人喜欢symmetric coroutine,可以自己简单的进行一下封装。
couroutine的一个典型的例子就是producer-consumer问题。我们来假设有这样两个函数,一个不停的produce一些值出来(例如从一个file中不停地读),另一个不断地consume这些值(例如,写入到另一个file中)。这两个函数的样子应该如下:
这两个函数都不停的在执行,那么问题来了,怎么来匹配send和recv呢?究竟谁先谁后呢?
coroutine提供了解决上面问题的一个比较理想的工具resume-yield。我们还是不说废话,先看看代码再来说说我自己的理解:
程序先调用consumer, 然后recv函数去resume唤醒producer,produce一个值,send给consumer,然后继续等待下一次resume唤醒。看下下面的这个示例应该就很明白了:
我们可以继续扩展一下上面的例子,增加一个filter,在producer和consumer之间做一些数据转换啥的。那么filter里都做些什么呢?我们先看一下没加filter之前的逻辑,基本就是producer去send,send to consumer,consumer去recv,recv from producer,可以这么理解吧。加了filter之后呢,因为filter需要对data做一些转换操作,因此这时的逻辑为,producer去send,send tofilter,filter去recv,recv from producer,filter去send,send to consumer,consumer去recv,recv fromfilter。红色的部分是跟原来不同的。此时的代码如下:
看完上面的例子,你是否想起了unix中的pipe?coroutine怎么说也是multithreading的一种。使用pipe,每个task得以在各自的process里执行,而是用coroutine,每个task在各自的coroutine中执行。pipe在writer(producer)和reader(consumer)之间提供了一个buffer,因此相对的运行速度还是相当可以的。这个是pipe很重要的一个特性,因为process间通信,代价还是有点大的。使用coroutine,不同task之间的切换成本更小,基本上也就是一个函数调用,因此,writer和reader几乎可以说是齐头并进了啊。
我们可以把迭代器 循环看成是一个特殊的producer-consumer例子:迭代器produce,循环体consume。下面我们就看一下coroutine为我们提供的强大的功能,用coroutine来实现迭代器。
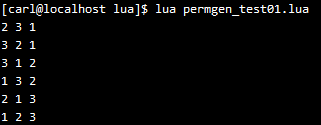
我们来遍历一个数组的全排列。先看一下普通的loop实现,代码如下:
运行结果如下:
再看一下迭代器实现,注意比较下代码的改变的部分:
运行结果如下:

permutations 函数使用了一个Lua中的常规模式,将在函数中去resume一个对应的coroutine进行封装。Lua对这种模式提供了一个函数coroutine.wap 。跟create 一样,wrap 创建一个新的coroutine ,但是并不返回给coroutine,而是返回一个函数,调用这个函数,对应的coroutine就被唤醒去运行。跟原来的resume 不同的是,该函数不会返回errcode作为第一个返回值,一旦有error发生,就退出了(类似C语言的assert)。使用wrap, permutations可以如下实现:
wrap 比create 跟简单,它实在的返回了我们最需要的东西:一个可以唤醒对应coroutine的函数。 但是不够灵活。没有办法去检查wrap 创建的coroutine的status, 也不能检查runtime-error(没有返回errcode,而是直接assert)。
从我们前面所写的可以看到,coroutine运行一系列的协作的多线程。每个coroutine相当于一个thread。一个yield-resume对可以在不同的thread之间切换控制权。但是,跟常规的multithr不同,coroutine是非抢占式的。一个coroutine在运行的时候,不可能被其他的coroutine从外部将其挂起,只有由其本身显式地调用yield才会挂起,并交出控制权。对一些程序来说,这没有任何问题,相反,因为非抢占式的缘故,程序变得更加简单。我们不需要担心同步问题的bug,因为在threads之间的同步都是显式的。我们只需要保证在对的时刻调用yield就可以了。
但是,使用非抢占式multithreading,不管哪个thread调用了一个阻塞的操作,那么整个程序都会被阻塞,这是不能容忍的。由于这个原因,很多程序员并不认为coroutine可以替代传统的multithreading。但是,下面我们可以看到一个有趣的解决办法。
一个很典型的multithreading场景:通过http下载多个remote files。我们先来看下如何下载一个文件,这需要使用LuaSocket库,如果你的开发环境没有这个库的话,可以看下博主的另一篇文章Lua基础 安装LuaSocket,了解下如何在Linux上安装LuaSocket. 下载一个file的lua代码如下:
运行结果有点长,不方便截图,就不贴了。
现在我们就知道怎么下载一个文件了。现在回到前面说的下载多个remote files的问题。当我们接收一个remote file的时候,程序花费了大多数时间去等待数据的到来,也就是在receive函数的调用是阻塞。因此,如果能够同时下载所有的files,那么程序的运行速度会快很多。下面我们看一下如何用coroutine来模拟这个实现。我们为每一个下载任务创建一个thread,在一个thread没有数据可用的时候,就调用yield 将程序控制权交给一个简单的dispatcher,由dispatcher来唤醒另一个thread。下面我们先把之前的代码写成一个函数,但是有少许改动,不再将file的内容输出到stdout了,而只是间的的输出filesize。
上面代码中有个函数receive ,相当于下载单个文件中的实现如下:
但是,如果要同时下载多文件的话,这个函数必须非阻塞地接收数据。在没有数据接收的时候,就调用yield挂起,交出控制权。实现应该如下:
settimeout(0)将这个连接设为非阻塞模式。当status变为“timeout”时,意味着该操作还没完成就返回了,这种情况下,该thread就yield。传递给yield的non-false参数,告诉dispatcher该线程仍然在运行。注意,即使timeout了,该连接还是会返回它已经收到的东西,存在partial变量中。
下面的代码展示了一个简单的dispatcher。表threads保存了一系列的运行中的thread。函数get 确保每个下载任务都单独一个thread。dispatcher本身是一个循环,不断的遍历所有的thread,一个一个的去resume。如果一个下载任务已经完成,一定要将该thread从表thread中删除。当没有thread在运行的时候,循环就停止了。
最后,程序创建它需要的threads,并调用dispatcher。例如,从w3c网站下载四个文档,程序如下所示:
我的程序运行了10s左右,4个文件已经下载完成,运行结果如下:

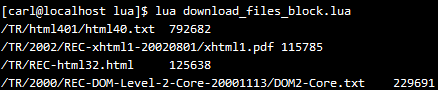
我又重新用阻塞式的顺序下载重试了一下,需要时间12s多一点,可能文件比较小,也不够多,对比不是很明显,阻塞的多文件下载代码如下,其实就是上面几段代码放在一块了
运行结果如下,跟上面的非阻塞式有点不同,下载完成的顺序,就是代码中写的顺序:
既然速度没有明显的更快,那么有没有优化空间呢,答案是,有。当没有thread有数据接收时,dispatcher遍历了每一个thread去看它有没有数据过来,结果这个过程比阻塞式的版本多耗费了30倍的cpu。
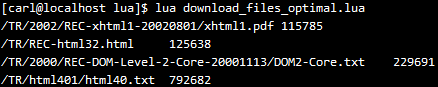
为了避免这个情况,我们使用LuaSocket提供的select函数。它运行程序在等待一组sockets状态改变时阻塞。代码改动比较少,在循环中,收集timeout的连接到表connections 中,当所有的连接都timeout了,dispatcher调用select 来等待这些连接改变状态。该版本的程序,在博主开发环境测试,只需7s不到,就下载完成4个文件,除此之外,对cpu的消耗也小了很多,只比阻塞版本多一点点而已。新的dispatch代码如下:
运行结果如下:

.jpg)
热烈欢迎各位留言,本人会虚心听取各位意见!